Table of Contents
Heart disease is a major health concern worldwide and remains one of the leading causes of death across various populations. This broad category of conditions affects the heart and blood vessels, with complications that can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other severe cardiovascular issues. Despite its prevalence, heart disease often develops silently, making early detection crucial for effective management and improved outcomes.
Recognizing the subtle signs of heart disease before they escalate can significantly enhance the chances of successful treatment and prevent severe health crises. Many individuals are unaware of these early warning signals or may dismiss them as inconsequential, which can delay critical intervention and increase the risk of adverse events.
The purpose of this blog is to shed light on the often-overlooked early signs of heart disease that should not be ignored. By increasing awareness and understanding of these symptoms, we aim to empower readers to seek timely medical advice and adopt preventive measures, ultimately contributing to better heart health and a reduced risk of serious complications.
Understanding Heart Disease
Definition and Types of Heart Disease
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease, encompasses a range of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. It primarily involves issues with the heart’s ability to function properly and can lead to serious health complications. The most common types of heart disease include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque (a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other substances). This can lead to chest pain (angina) or heart attacks.
- Heart Failure: Also known as congestive heart failure, this condition arises when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, causing fluid to accumulate in the lungs and other parts of the body.
- Arrhythmias: These are irregular heartbeats that can range from harmless to life-threatening. Common arrhythmias include atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and bradycardia.
- Valvular Heart Disease: This involves damage to or a defect in one or more of the heart’s valves, which can affect blood flow through the heart. Conditions such as aortic stenosis and mitral regurgitation fall into this category.
- Congenital Heart Defects: These are structural problems with the heart that are present at birth. Examples include septal defects and coarctation of the aorta.
- Pericarditis: This is inflammation of the pericardium, the sac-like membrane surrounding the heart, which can cause chest pain and other symptoms.
Overview of Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing heart disease. These risk factors are often categorized into modifiable and non-modifiable types:
- Genetics: A family history of heart disease can increase an individual’s risk. Genetic predisposition plays a role in conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol, which are linked to heart disease.
- Lifestyle: Daily habits significantly impact heart health. Sedentary behavior, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can all elevate the risk of heart disease.
- Diet: A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can contribute to the development of heart disease. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential for heart health.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces blood pressure, and improves cholesterol levels, thereby lowering the risk of heart disease.
- Obesity: Excess body weight is associated with increased risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure) and diabetes can significantly increase the risk of heart disease if not managed properly.
Understanding these factors and their interplay helps in recognizing the importance of prevention and early intervention in heart disease. Managing risk factors through lifestyle changes and medical care can greatly reduce the likelihood of developing heart disease or mitigate its impact if it occurs.
Common Early Signs of Heart Disease
Recognizing early signs of heart disease is crucial for timely intervention and effective treatment. Some symptoms may be subtle or easily attributed to other causes, but they should not be dismissed. Here’s a closer look at common early signs of heart disease:
Chest Discomfort
- Heartburn vs. Angina: Chest discomfort can sometimes be mistaken for heartburn, but distinguishing between the two is essential. Heartburn often results from acid reflux and is typically a burning sensation that occurs after eating. Angina, on the other hand, is chest pain or discomfort caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. It may feel like pressure, squeezing, or heaviness and can radiate to the shoulders, neck, or jaw. Angina may occur during physical activity or stress and usually subsides with rest or medication.
Shortness of Breath
- Unexplained or Persistent Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially when it occurs unexpectedly or persists, can be a sign of heart disease. This symptom may manifest during physical activity or even at rest. It could indicate heart failure or other heart conditions where the heart is struggling to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid accumulation in the lungs.
Fatigue
- Chronic Tiredness: Unexplained, persistent fatigue is a common early warning sign of heart disease. Unlike typical tiredness that results from a busy day or lack of sleep, this type of fatigue is often persistent and disproportionate to the level of exertion. It can be a sign that the heart is not pumping blood efficiently, affecting overall energy levels and causing feelings of exhaustion.
Palpitations
- Irregular or Rapid Heartbeats: Palpitations refer to the sensation of feeling your heart pounding, fluttering, or beating irregularly. While occasional palpitations may be benign, frequent or severe palpitations can indicate arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) or other underlying heart issues. It’s important to monitor these symptoms and seek medical advice if they occur regularly or are accompanied by other symptoms like dizziness or chest pain.
Dizziness or Lightheadedness
- Potential Link to Heart Issues: Feeling dizzy or lightheaded can be related to heart disease, especially if it occurs alongside other symptoms. This can be due to a reduced blood flow to the brain, which may result from heart arrhythmias, heart failure, or other cardiovascular problems. If these episodes are frequent or severe, they warrant a medical evaluation.
Swelling in the Legs, Ankles, or Feet
- Possible Sign of Heart Failure: Swelling in the lower extremities can be a symptom of heart failure or other cardiovascular conditions. When the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, fluid can accumulate in the legs, ankles, and feet. This swelling, known as edema, can be gradual and may be accompanied by other signs such as shortness of breath or weight gain.
Recognizing these early signs and understanding their potential implications can lead to timely medical intervention and improved management of heart disease. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine their cause and appropriate treatment.
Less Recognized Symptoms
While many people are familiar with the more obvious signs of heart disease, some symptoms can be less obvious and are often overlooked. Here’s a closer look at these less recognized symptoms:
Nausea and Indigestion
- Potentially Linked to Heart Issues: Nausea and indigestion can sometimes be associated with heart disease, particularly in women. Unlike typical gastrointestinal issues, these symptoms may be accompanied by other signs such as chest discomfort or shortness of breath. In some cases, nausea and indigestion can signal a heart attack, especially if they occur suddenly and without an apparent cause.
Sweating and Cold Clammy Skin
- Unexplained Sweating as a Symptom: Profuse sweating, particularly if it occurs without a clear reason, can be an early indicator of heart problems. Cold, clammy skin can also be a sign of distress related to heart issues. This symptom may accompany other signs like chest pain or shortness of breath and can be indicative of a heart attack or severe cardiac distress.
Pain in Other Areas
- Pain Radiating to the Back, Neck, or Jaw: While chest pain is a common symptom of heart disease, pain that radiates to other areas of the body can also be a sign. This includes pain extending to the back, neck, jaw, or even the arms. Such pain may be less severe than the chest pain but can be a warning sign of a heart attack or angina. It’s important to consider these symptoms in conjunction with other signs of heart disease.
Sleep Disturbances
- Sleep Apnea and Its Link to Heart Disease: Sleep disturbances, particularly sleep apnea, can be associated with an increased risk of heart disease. Sleep apnea is a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, leading to fragmented sleep and low oxygen levels. This condition can contribute to high blood pressure, arrhythmias, and other cardiovascular issues. People experiencing excessive daytime sleepiness, loud snoring, or choking sensations during sleep should consider a sleep study to evaluate for sleep apnea and its potential impact on heart health.
Understanding these less recognized symptoms is crucial for early detection and management of heart disease. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they occur alongside more common signs of heart issues, it’s important to seek medical advice to ensure timely evaluation and treatment.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Preventing heart disease involves addressing various risk factors and making proactive lifestyle changes. Understanding these aspects is essential for maintaining heart health and reducing the likelihood of developing cardiovascular conditions. Here’s an overview of key prevention strategies:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Diet: A heart-healthy diet is crucial for reducing the risk of heart disease. Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Reducing intake of saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can help manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Foods high in fiber, such as oats, beans, and nuts, are beneficial for heart health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart, improves circulation, and helps manage weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week. Activities like walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming are excellent for cardiovascular fitness.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease as it damages the blood vessels and raises blood pressure. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall health. Seek support through cessation programs, counseling, or medications if needed to overcome nicotine addiction.
Regular Check-ups
- Importance of Routine Medical Exams: Regular medical check-ups are vital for early detection and management of heart disease. Routine visits to a healthcare provider allow for the monitoring of heart health, assessment of risk factors, and early intervention if any issues are detected. These check-ups typically include blood pressure measurements, cholesterol testing, and a review of overall health and lifestyle.
Monitoring Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
- Blood Pressure: High blood pressure (hypertension) is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Regular monitoring helps ensure that blood pressure levels are within a healthy range. Lifestyle changes, such as reducing sodium intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular exercise, can help manage blood pressure. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to keep blood pressure under control.
- Cholesterol: Monitoring cholesterol levels is crucial for heart health. High levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease. Regular blood tests can assess cholesterol levels, and managing them through diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medication can help reduce cardiovascular risk.
By addressing these risk factors and adopting preventive measures, individuals can significantly lower their chances of developing heart disease. Making informed lifestyle choices, staying on top of regular check-ups, and monitoring key health metrics are essential steps in maintaining a healthy heart and preventing cardiovascular issues.
When to Seek Medical Help
Recognizing when to seek medical help is crucial for addressing heart disease effectively and preventing serious complications. Understanding the urgency of symptoms, the importance of timely consultation, and the diagnostic tools available can significantly impact treatment outcomes. Here’s a detailed look at these aspects:
Recognizing the Urgency of Symptoms
- Immediate Attention for Severe Symptoms: If you experience severe symptoms such as intense chest pain, severe shortness of breath, or sudden dizziness, seek emergency medical attention immediately. These could be signs of a heart attack or other acute cardiac events. Symptoms that come on suddenly and are severe warrant immediate evaluation to prevent potentially life-threatening complications.
- Persistent or Worsening Symptoms: Even if symptoms are not severe, persistent or worsening signs, such as ongoing chest discomfort, frequent palpitations, or unusual fatigue, should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Early detection and treatment can prevent the progression of heart disease and reduce the risk of more serious problems.
Importance of Timely Consultation with a Healthcare Professional
- Early Diagnosis and Management: Consulting with a healthcare professional when experiencing symptoms or having risk factors is essential for early diagnosis and management of heart disease. Regular check-ups and prompt evaluation of symptoms can lead to early treatment, which is crucial for improving outcomes and managing the condition effectively.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: A healthcare provider can develop a personalized treatment plan based on your specific symptoms, risk factors, and overall health. This may include lifestyle modifications, medication, or other interventions tailored to your needs.
Overview of Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart and is commonly used to detect arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac conditions. It provides a visual representation of the heart’s rhythm and can help identify abnormal patterns.
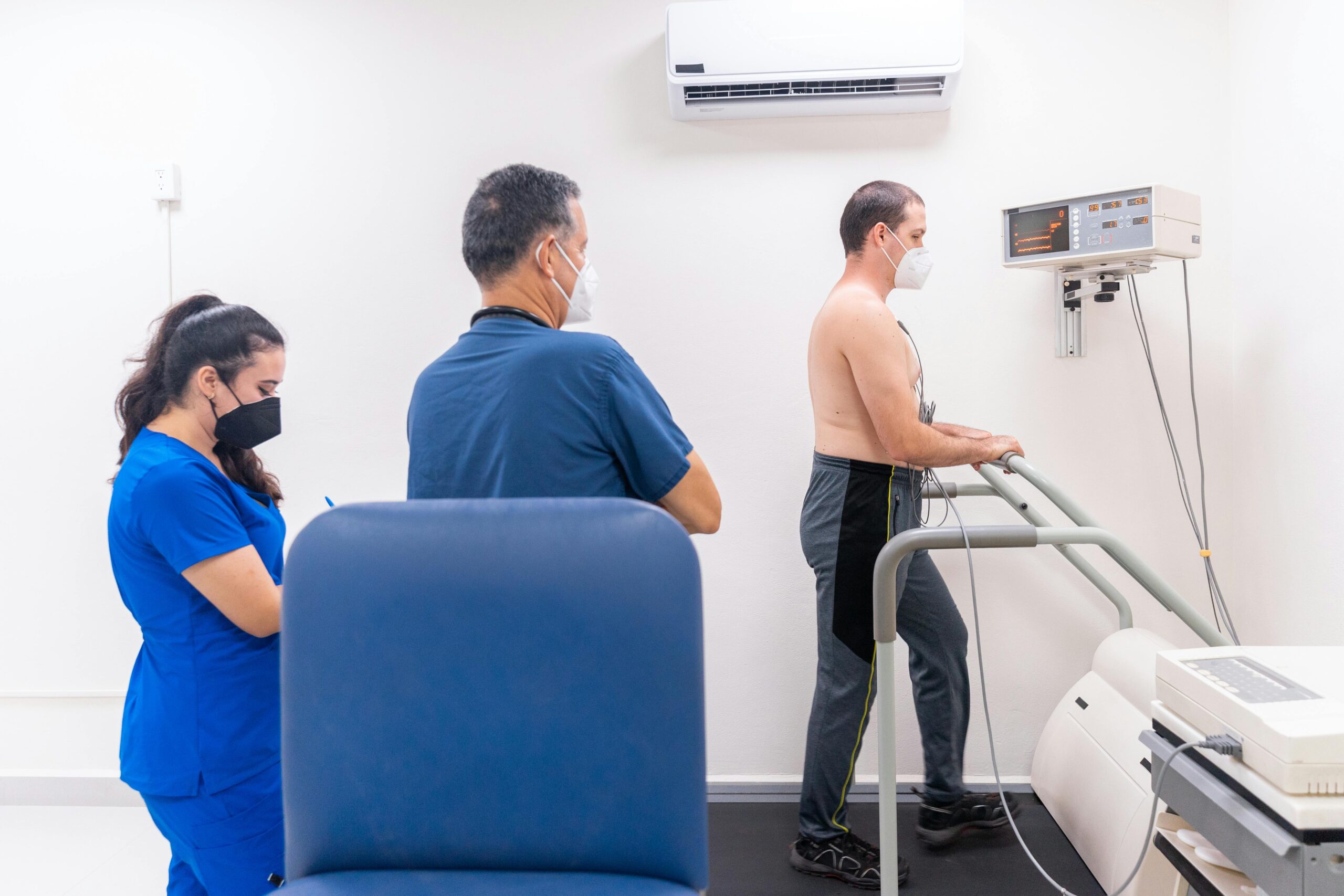
- Stress Test: A stress test, often performed on a treadmill or stationary bike, assesses how the heart responds to physical exertion. It can help identify issues with blood flow to the heart, such as coronary artery disease, by monitoring heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG changes during exercise.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test uses sound waves to create images of the heart’s structure and function. It can help evaluate the heart’s chambers, valves, and overall pumping ability, and is useful for diagnosing conditions like heart failure and valvular heart disease.
- Holter Monitor: A Holter monitor is a portable ECG device worn for 24 to 48 hours to continuously record the heart’s electrical activity. It is used to detect irregular heartbeats or arrhythmias that may not be evident during a standard ECG.
- Cardiac Catheterization: This invasive procedure involves threading a catheter through blood vessels to the heart to examine the coronary arteries and heart chambers. It can help diagnose blockages or narrowing in the arteries and may be followed by interventions such as angioplasty or stent placement.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can measure levels of certain markers, such as cholesterol and troponin (a protein released during a heart attack), to assess heart health and identify potential issues.
Seeking timely medical help and undergoing appropriate diagnostic tests are essential for effective management and treatment of heart disease. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes and reduce the risk of severe complications. If you experience any concerning symptoms or have risk factors for heart disease, consult a healthcare professional promptly to ensure proper evaluation and care.
Living with Heart Disease
Managing heart disease involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and support systems to maintain overall health and quality of life. Here’s an overview of how to manage the condition effectively and access the support you may need:
Managing the Condition with Medication and Lifestyle Changes
- Medication:
- Prescription Drugs: Medications play a crucial role in managing heart disease. Common types include:
- Statins: To lower cholesterol levels.
- Beta-Blockers: To reduce heart workload and lower blood pressure.
- ACE Inhibitors: To help relax blood vessels and reduce blood pressure.
- Diuretics: To reduce fluid buildup in cases of heart failure.
- Antiplatelet Agents: To prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
- Adherence: Following your healthcare provider’s medication regimen is vital for controlling symptoms and preventing complications. Regularly reviewing and adjusting medications as needed is also important.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Diet: Adopting a heart-healthy diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is crucial. Limiting saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars helps manage cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens the heart and improves overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, tailored to your health status and ability.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce the strain on the heart and manage risk factors like high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is essential for heart health and can significantly reduce the risk of worsening heart disease.
- Alcohol Moderation: Limiting alcohol consumption can help manage blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health.
Support Systems and Resources for Patients
- Healthcare Team: Building a supportive relationship with a healthcare team, including cardiologists, primary care physicians, dietitians, and exercise specialists, is essential for effective management of heart disease. Regular check-ups and open communication with your healthcare providers help ensure optimal treatment and care.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs: These programs offer structured exercise, education, and support for individuals recovering from heart events or managing heart disease. They provide a safe environment to improve cardiovascular health and learn strategies for long-term management.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups for individuals with heart disease can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community. Sharing experiences with others who understand the challenges of living with heart disease can be encouraging and empowering.
- Educational Resources: Access to educational materials about heart disease, treatment options, and healthy living can help patients make informed decisions and manage their condition effectively. Resources may include books, online articles, and informational websites provided by reputable health organizations.
- Mental Health Support: Dealing with a chronic condition like heart disease can be emotionally challenging. Seeking counseling or therapy to address stress, anxiety, or depression is important for overall well-being. Mental health support can complement physical health efforts and improve quality of life.
Living with heart disease requires a proactive approach to managing both medical and lifestyle aspects of the condition. By adhering to prescribed treatments, making healthy lifestyle choices, and utilizing available support systems and resources, individuals with heart disease can lead fulfilling and healthier lives.
Conclusion
Understanding and recognizing the early signs of heart disease is crucial for improving health outcomes and preventing serious complications. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can significantly enhance the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the risk of severe heart-related issues.
By paying attention to symptoms such as chest discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, and less commonly recognized signs like nausea or unexplained sweating, individuals can take proactive steps to address potential heart health concerns. Awareness of these signs, coupled with an understanding of risk factors and preventive measures, empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Staying informed about heart health and actively engaging in preventive practices, such as maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle, monitoring key health metrics, and adhering to prescribed treatments, is essential for managing and reducing the risk of heart disease. Regular medical check-ups play a pivotal role in monitoring heart health and catching any potential issues early.
As a call to action, we encourage you to schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to stay on top of your heart health. If you experience any concerning symptoms or have risk factors for heart disease, don’t hesitate to consult with a medical professional. Taking these steps can help ensure that you receive timely care and maintain a heart-healthy lifestyle, ultimately contributing to better long-term health and well-being.
Additional Resources
To further support your understanding and management of heart disease, here are some valuable resources and materials that provide comprehensive information, support, and guidance:
Links to Heart Disease Resources and Support Organizations
- American Heart Association (AHA): The AHA offers a wealth of information on heart disease prevention, treatment, and research. Their website provides educational materials, guidelines for healthy living, and resources for finding support and medical care.
- American Heart Association
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Heart Disease: The CDC provides data, educational resources, and preventive strategies related to heart disease. Their site includes information on risk factors, symptoms, and ways to reduce heart disease risk.
- CDC – Heart Disease
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): NHLBI offers detailed information on heart disease, including research findings, educational materials, and tools for managing and preventing cardiovascular conditions.
- NHLBI – Heart Disease
- American College of Cardiology (ACC): The ACC provides resources for both patients and healthcare professionals on the latest advancements in cardiology, heart disease management, and educational materials.
- American College of Cardiology
- Heart Foundation: This organization provides support and education on heart disease, offering information on managing the condition, living a heart-healthy lifestyle, and connecting with local support networks.
- Heart Foundation
Suggested Reading and Further Educational Material
- Books:
- “The Heart Disease Breakthrough” by Dr. William Davis: This book explores the connection between heart disease and dietary factors, offering practical advice for improving heart health through nutrition.
- “Prevent and Reverse Heart Disease” by Dr. Caldwell Esselstyn: Focuses on lifestyle changes and plant-based diets to prevent and reverse heart disease, providing evidence-based strategies for heart health.
- Articles and Journals:
- “Journal of the American College of Cardiology”: A peer-reviewed journal offering the latest research and advancements in cardiology, including studies on heart disease prevention and treatment.
- “Circulation”: Published by the American Heart Association, this journal provides research articles and clinical studies on cardiovascular health and disease.
- Online Courses and Webinars:
- Coursera and edX: These platforms often offer courses related to heart health, including topics on cardiovascular disease prevention, treatment, and overall wellness.
- American Heart Association Webinars: Provides access to webinars on various aspects of heart health, from understanding heart disease to implementing lifestyle changes.
By exploring these resources and educational materials, you can gain a deeper understanding of heart disease, access support networks, and stay informed about the latest advancements in cardiovascular health.